Radiation biology in space
Interest in space exploration interest has escalated with multiple launches occurring for space travel, including space tourism, as well as preparation for manned missions to Mars.
As Australia’s premier organisation for providing and characterising different types of high-intensity irradiation, ANSTO has developed a sovereign capability for understanding space-related radiation effects on living organisms.
ANSTO scientists from the Centre for Accelerator Science and the Department of Human Health support investigations to understand the impacts and effects of ionising radiation on living biological systems to help develop mitigation and protection strategies to protect the health of astronauts and space travellers.
Collaborators include the French Space Agency, INSERM U1296: Radiation, Defence, Health and Environment and the Australian Space Agency.
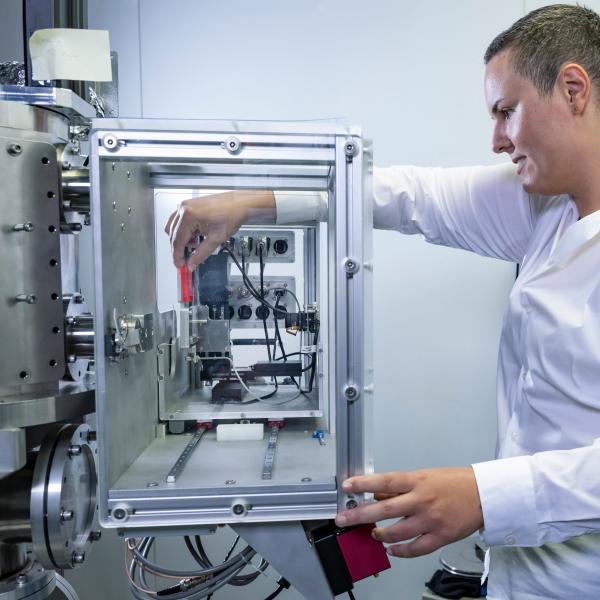

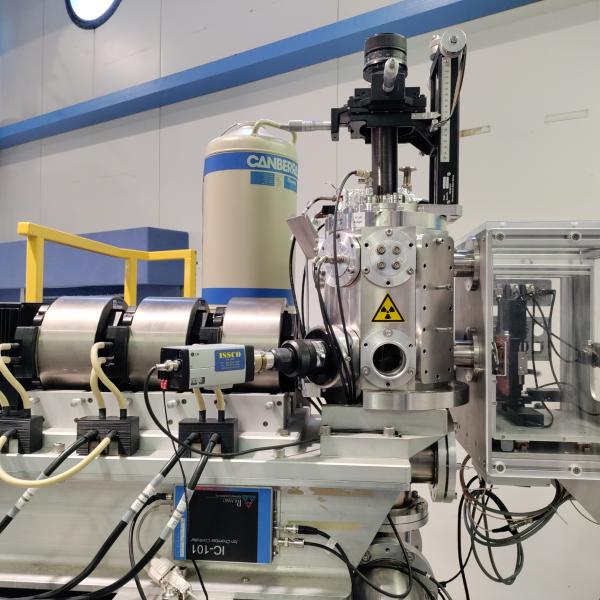
Irradiation Facility
The ANTARES 10MV accelerator is equipped with the Heavy Ion Nuclear Microprobe, the only instrument in Australia capable of focusing light and heavy ion beams down to a micron-size spot. The ion microbeam is extracted in air, allowing irradiation of living samples with a wide range of ion species and fluxes and with dose rates from mGy/s to G/s. The flexible and unique system allows irradiation of samples of dimension from µm2 to cm2.
The ANSTO facilities and capabilities are well suited for irradiation of human, animal or plant cells with potential research applications in radiobiology for harsh radiation environments, such as space or nuclear plants; fundamental radiobiology, cancer research and particle therapy, drug development as countermeasures, and dosimetry.
Radiobiology Facilities
Radiobiology facilities include PC1 and 2 laboratories to support for pre- and post-handling of biological samples.
The available cell-based capabilities see survival, proliferation, damage/repair, Reactive Oxygen Species, molecular biology, biochemistry and pharmacology.
Scientists can access to analysis such as immunohistochemistry, flow cytometry, and fluorescence microscopy.
Finally, the facilities provide access to other radiation sources such as X-rays, gamma-rays and neutrons.