In late December 2020, ANSTO renewed its longstanding Commercial Agreement with the National Synchrotron Radiation Research Center (NSRRC) in Taiwan to continue its operation of the Sika triple-axis spectrometer at the Australian Centre for Neutron Scattering and station scientific and technical staff at ANSTO.
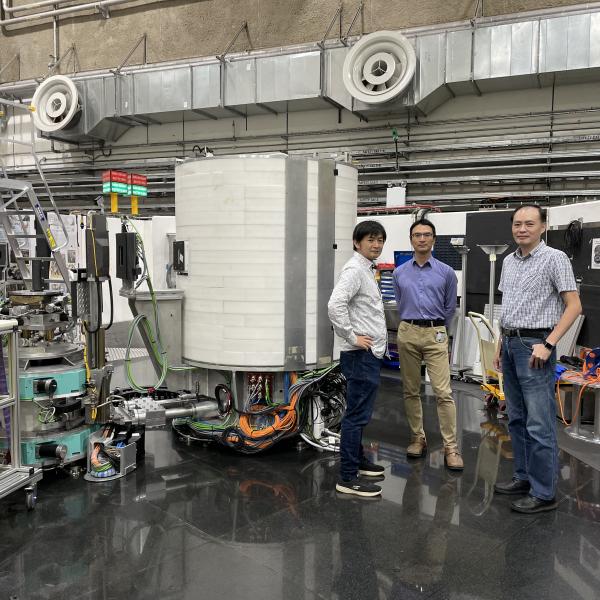
Sika, which is named after a species of deer found in Taiwan, uses cold neutrons produced by the OPAL multipurpose reactor, in a technique to characterise the properties of materials, including quantum effects.
ANSTO Acting CEO Shaun Jenkinson and NSRRC Director Gwo-Huei Luo signed the Agreement during a virtual video conference linking Australia and Taiwan on 18 December.

NSRRC Director Gwo-Huei Luo signs the agreement during a virtual event

Acting CEO Shaun Jenkinson (centre) signs agreement on behalf of ANSTO with International Affairs Manager Mark Alexander (left) and Leader of the Australian Centre for Neutron Scattering, Dr Jamie Schulz
The renewed Agreement is expected to further facilitate research collaboration, foster scientific expertise in neutron science and enhance Australia and Taiwan’s strengths in science and technology.
Under the Agreement, NSRRC staff at ANSTO and other Taiwanese researchers have access to Sika and other neutron beam instruments.
“In a win-win situation, ANSTO is also able utilise Sika. The Agreement allows Australian and international researchers to submit a proposal to use the Sika instrument for experiments,” said Dr Jamie Schulz, Leader, Australian Centre for Neutron Scattering.
The renewed Agreement will build on a productive and mutually beneficial relationship established by the first Agreement signed in 2013.
Since the initial Agreement, the NSRRC had made a substantial effort and investment to optimise Sika’s operation and equipment, which allows scientists to conduct experiments in a more accessible and efficient manner.
Over the past few years, more than 50 Taiwanese research teams have used Sika and other neutron beam instruments for their studies producing approximately 20 publications annually.
Read about recent research on the Sika instrument.