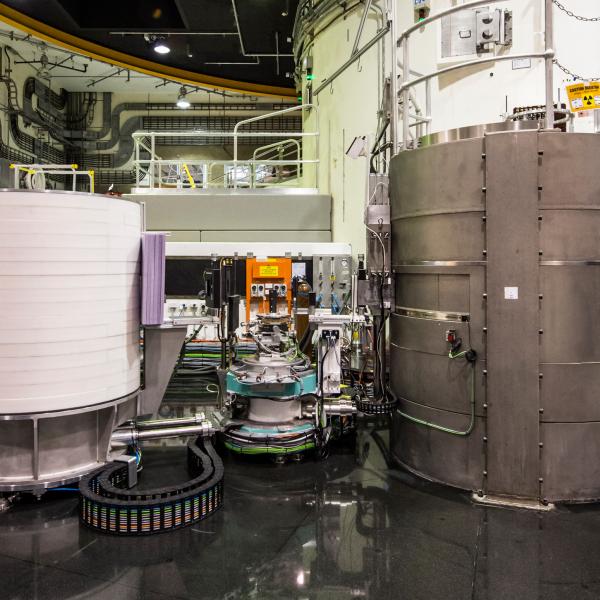
Sika - Cold Triple Axis Spectrometer
Triple-axis or 3-axis spectrometers were originally developed by Bert Brockhouse at Chalk River in Canada. He was awarded the Nobel Prize in part for this invention, along with the constant-Q method of operation and other seminal experiments .
To provide Taiwanese users with a world-class neutron experimental facility, the Ministry of Science and Technology (formally the National Science Council) funded the construction of a cold neutron triple-axis spectrometer, which was carried out by the National Central University. The Taiwan-Australian neutron instrument Sika is located in the Neutron Guide Hall at ANSTO's Lucas Heights campus. NSRRC took over the instrument in 2013 , commissioned the instrument and introduced it into the international user program. NSRRC is also responsible for the promotion of neutron research and user cultivation in Taiwan.
The project to construct the cold neutron, triple-axis spectrometer named Sika was completed at the end of 2012. In 2013, National Central University handed over the instrument to the National Synchrotron Radiation Research Center to lead the commissioning and user program. The first call for proposals went out in 2014, officially opening the instrument to domestic and international users.
SIKA is equipped with a large (230 x 252 mm2) double-focusing graphite monochromators to provide a large neutron flux on samples. A 13 blade horizontal focusing graphite analyser combined with He-3 tube or a one-dimensional position sensitive detector (48 wires) provides for great flexibility.
The combination of high neutron flux, good energy and momentum resolution, low background and a large dynamic range make Sika ideally suited to study of spin and lattice dynamics, magnon and phonon dispersion relations in single crystal samples Relaxation phenomena, critical scattering, soft-modes, and relaxation-effects in complex fluids, magnetism, ionic conductors, catalysts, H storage and functional energy-related materials also play an important role in the science output of the instrument.
The instrument is named after the East Asian deer Sika Cervus nippon.