
Radon analytical facilities
Radon is a naturally-occurring radioactive trace gas of terrestrial origin.
As an unambiguous tracer of terrestrial influence on air mass composition, radon is an essential component of baseline studies for:
- the selection of least terrestrially perturbed marine air masses
- tracing and analysis of air mass history and fetch;
- calibration/constraint of regionally-integrated emission estimates for important distributed trace gases; and
- an evaluation of transport and mixing schemes in climate and chemical transport models.
The Radon Analytical Laboratory operates a comprehensive suite of instrumentation for the monitoring and analysis of natural radioactivity resulting from radon (222Rn), thoron (220Rn) and their progeny.
The facility’s capabilities include measuring an extended range of radon and radon progeny concentrations in indoor or outdoor air; in situ radon and thoron emanation from rocks and soils; and radon exhalation rates from gaseous, liquid, solid and mixed phase samples.
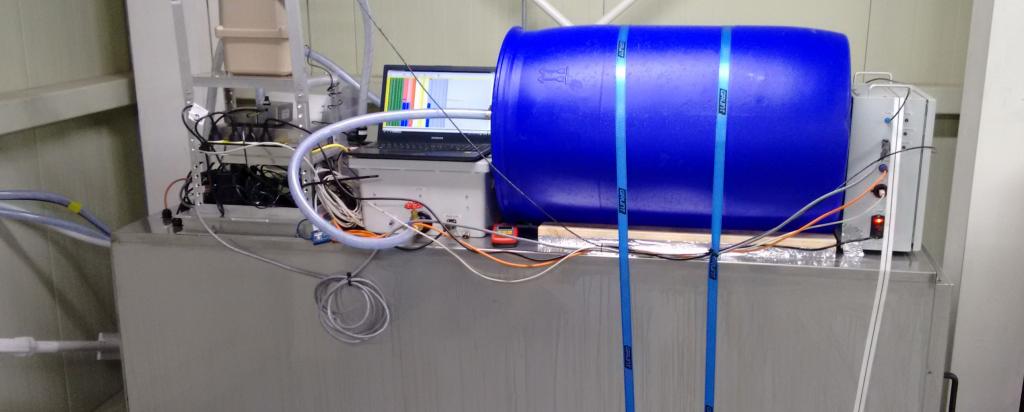
Radon analytical and monitoring facilities include radon concentration measurements using the “Radon Rig”. Built at ANSTO, the radon rig is designed to measure very low radon concentrations in, and radon exhalation from, either solid, liquid or gaseous samples under normal pressures.

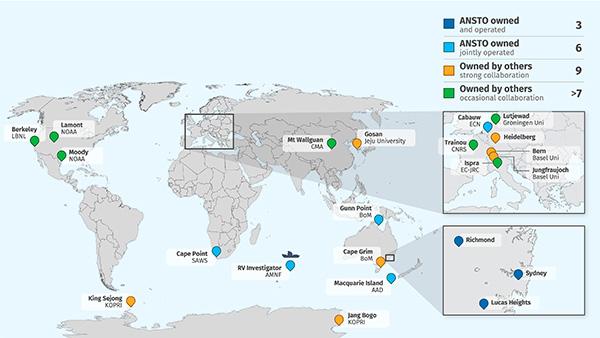
Radon is collected at sites around the world including Cape Grim Station in Tasmania, Macquarie Island, Cape Point, including Mauna Loa Observatory in Hawaii, Cape Point Observatory in South Africa, Gosan Island in South Korea, Jungfraujoch in the Swiss Alps, King Sejong Station in Antarctica and Mt Waliguan in Tibet and aboard the Australian National Marine Facility RV Investigator.
ANSTO also builds and deploys tower-based and airborne instruments to measure vertical radon variations through the lower atmosphere.
Dual flow loop, two-filter radon detector
ANSTO's unique technology for highly sensitive measurements of atmospheric radon is recognised by the World Meteorological Organisation as the best in the world for global and atmospheric compositional baseline studies.

Two models (200 L and 1500 L) of semi-portable detectors are available for outdoor, continuous, hourly monitoring of ambient radon in air. These detectors, which can be maneuvered by 2-4 persons (<3m long; <100kg), can be deployed to most field sites for either short-term (several weeks), or semi-permanent, monitoring.
