
Proton Elastic Scattering
Physical Principles
Proton elastic scattering (PESA) is ideally suited for measurement of hydrogen concentration in thin samples, such as aerosols. An example of PESA spectrum of a thin aerosol sample deposited on Teflon filter is shown in Figure 1.
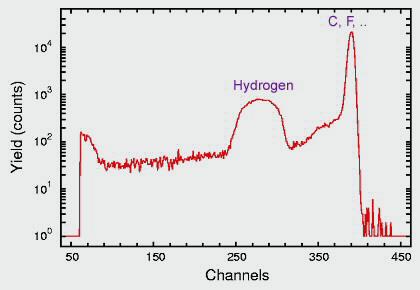
In an Ion Beam Analysis laboratory PESA spectra are acquired at 30 degrees which provide well resolved H peak. Calibration is performed by using thin Mylar sheets (35 micrograms/cm2) which has well-known hydrogen concentration. The background-subtracted peak area was found to be proportional to the hydrogen concentration over the concentration range 0-200 micrograms/cm2. Typically minimum detection limits of the order of 0.2 micrograms/cm2 were obtained for 3 µC runs corresponding to approximately 1 ng/m3 of hydrogen in the air.