
Published on the 15th June 2017 by ANSTO Staff
ANSTO, in association with James Cook University in QLD, has collected marine sediments from the Australia Pacific Region which will be used to produce Certified Reference Materials (CRMs) by the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) Environmental Laboratories Monaco.
“These sediments join a carefully selected set of global archive samples which provide a record of the earth’s current conditions and ensure quality control when measuring contaminants and trace elements in sediment, seawater and marine organisms,” said Mat Johansen, a senior researcher who specialises in environmental contaminants.
Johansen and Michael Corry (below right) from ANSTO and James Daniell from James Cook University collected the CRM samples under an IAEA project, in coordination with Australian federal agencies.
Marine sediments are important in that they provide a base to marine food webs. They also provide a record of natural and human processes.
“The IAEA wanted samples with trace contaminants, but that were not heavily polluted. They also wanted relatively high organic matter content that is typical of many coastal areas of Australasia” said Johansen.
 |
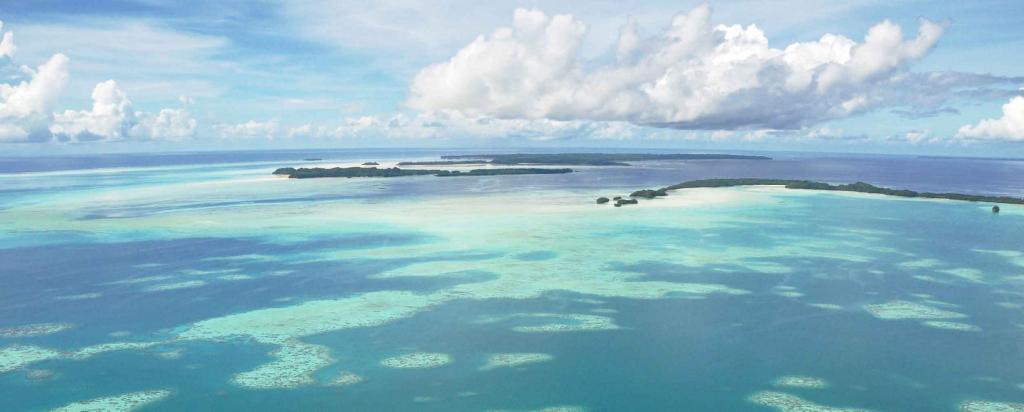
| Marine samples were collected within the Great Barrier Reef Park with permission. |
After reviewing more than 300 potential locations in consultation with the IAEA, the sediments were retrieved from six widely-spaced sites designed to capture a range of chemical signatures from different coastal features and nearby watersheds. All sites were close to the main Australian landmass, well within the Great Barrier Reef, where finer sediments are deposited.
“Working conditions were not ideal, with steady winds, rough seas, and long days of transit between sites. However, our hosts from James Cook University and boat crew were very reliable, professional and transported us safely to all work sites and helped us a great deal in gathering samples” said Johansen.
 The Great Barrier Reef Parks Authority gave permission for the collection of the sediments, which avoided coral, sea grasses and sensitive habitats. IAEA CRMs are vital for training programs, inter-comparison studies and to assist regional laboratories in maintaining their own quality control procedures.
|